Diamond
When choosing a diamond it is crucial to understand its worth and how its different characteristics will affect its appearance and value. An easy way to assess this is to follow the 4 C's, which was created by the GIA which stand for Cut, Clarity, Colour and Carat.

Cut
Of all the 4 Cs, cut has the greatest effect on a diamond’s beauty. In determining the quality of the cut, the grader evaluates the cutter’s skill in the fashioning of the diamond. The more precise the cut, the more captivating the diamond is to the eye.
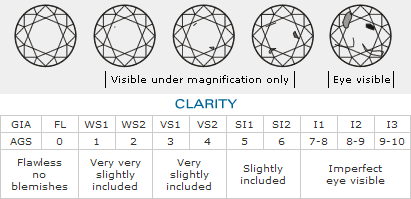
Clarity
Diamond clarity is the presence or absence of characteristics called inclusions in the diamond. When grading the clarity of a diamond, the lab determines the relative visibility of the inclusions in a diamond and their impact on the overall visual appearance. Diamond clarity is graded on a scale like this; Flawless, Internally Flawless, VVS1, VVS2, VS1, VS2, SI1, SI2, I1, I2, and I3.

Colour
The Colour of a diamond actually refers to the lack of colour in a diamond, with perfectly colourless diamonds considered the highest quality with the highest value, and brown or yellow diamonds being the lowest quality.

Carat
Carat is the unit of measurement for the physical weight of diamonds. One carat equals 0.200 grams or 1/5 gram and is subdivided into 100 points. For example, a 0.46ct diamond will be referred to as having 46 points. Large diamonds are rarer than smaller ones, and as the carat weight increases, the value of the diamond increases as well. However, the increase in value is not proportionate to the size increase. Two diamonds of equal weight may be unequal in value, depending upon other determining factors such as Cut, Colour and Clarity.
